The pictogram concept tends to be a confusing aspect of the GHS system, especially given its contextual use depending on the hazard category of a class, or specific target audience. To better aide ones understanding of pictograms, this guide serves to thoroughly explain the many GHS pictogram meanings; the starting point being defining what a pictogram actually is.
The 6th revised edition of The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals defines a pictogram as ‘a graphical composition that may include a symbol plus other graphic elements, such as a border, background pattern or colour that is intended to convey specific information.’ In terms of GHS’s hazard communications system, pictograms are required on the labels of hazardous chemical products, consisting of exact reproductions of the GHS prescribed black hazard symbols, on a white background contained within a wide, red and square-shaped frame that sits atop a single point. Use of pictograms on (M)SDSs need not be exact reproductions of that used on chemical labels, but some representation (the identification code, a written descriptor, the black hazard symbol) of it, which is to be provided in the Hazard Identification section. GHS pictogram meanings can be dissected through analysis of the graphical illustration used, the written descriptor of each symbol, and which hazards are to be associated with the overall pictogram. GHS pictogram meanings can also be differentiated into two pictogram sets that make use of the same hazard symbols. The pictogram description above comprises the set used for labels of hazardous chemicals used in the workplace; the other set, alters its use of colour and the way in which info is represented as it instead is used for the labelling of dangerous goods that are to be transported. This guide focuses on GHS pictogram meanings for pictograms that are to be put on labels of hazardous products used in the workplace.
The chart below lists which hazard classes, categories, and sub-categories are to be represented by a specific pictogram. A brief description of what the pictogram encompasses is also included.
|
Pictograms & Descriptions of the Hazardous Symbols |
Hazard Classes/Categories |
Sub-Categories |
|
Flammable
A material (gas, liquid, solid) that rapidly catches fire upon ignition or combustion |
Flammable Gases |
1 |
|
Flammable Aerosols |
1, 2 |
|
|
Flammable Liquids |
1, 2, 3 |
|
|
Flammable Solids |
1,2 |
|
|
Self-reactive Substance or mixtures |
B,C,D,E,F |
|
|
Pyrophoric Liquids |
1 |
|
|
Pyrophoric Solids |
1 |
|
|
Self-heating substances or mixtures |
1, 2 |
|
|
Substances which when in contact with water, emit flammable gases |
1, 2, 3 |
|
|
Organic Peroxides |
B, C, D, E, F, |
|
|
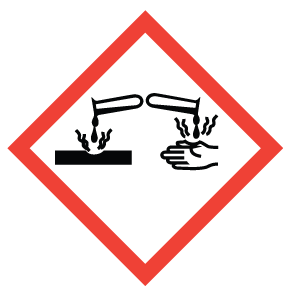
Corrosion
May be corrosive to metals; chemically reacts to damage or destroy other materials Skin Corrosion; irreversible damage to skin through chemical reactivity with substance, such that visible necrosis (cell death) causes ulcers, bleeding and bloody scabs to dermis |
Corrosive to Metals |
1 |
|
Flammable Gases |
2 |
|
|
Self-reactive substances and mixtures |
G |
|
|
Organic Peroxides |
G |
|
|
Skin Corrosion |
1A, 1B, 1C |
|
|
Serious Eye Damage |
1 |
|
|
Gas Cylinder
Represents any gases under pressure that are contained in a receptacle at a pressure of 200kPa or more at 20°C |
Compressed Gas |
|
|
Liquefied Gas |
||
|
Refrigerated Liquefied Gas |
||
|
Dissolved Gas |
||
|
Oxidizing
Any gas which may combine with oxygen to cause or contribute to combustion of other material more than the air does |
Oxidizing Gases |
1 |
|
Oxidizing Liquids |
1, 2, 3 |
|
|
Oxidizing Solids |
1, 2, 3 |
|
|
Explosives
A reactive substance that through its chemical reactivity is capable of producing a gas that can damage the surrounding environment due to its high temperature, pressure, and speed. Pyrotechnic substances are included despite lack of gas reactivity. |
Unstable Explosives |
|
|
Explosives |
Divisions 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 |
|
|
Self-reactive substances and mixtures |
A, B | |
| Organic Peroxides |
A, B |
|
|
Health Hazard
A chemical substance that upon exposure, may cause acute or chronic health effects as determined by statistically significant results from related studies |
Respiratory Sensitization |
1 |
|
Germ-cell Mutagenicity |
1A, 1B, 2 |
|
|
Carcinogenicity |
1A, 1B, 2 |
|
|
Reproductive Toxicity |
1A, 1B, 2 |
|
| Specific target organ toxicity following single exposure |
1, 2 |
|
|
Specific target organ toxicity following repeated exposure |
1, 2 |
|
|
Aspiration Hazard |
1, 2 |
|
|
Environmental Hazard
Chemical substance may contribute to disruption of aquatic ecosystems, unregulated bio- accumulation or availability, cause consequential effects to the ozone layer |
Acute hazards to aquatic environment | 1, 2 |
| Chronic hazards to aquatic environment |
1, 2 |
|
|
Skull and Crossbones – Toxic
Can cause death or toxicity upon oral, dermal, or inhaled exposure to small amount of substance even in a short duration of time |
Acute Toxicity – Oral, Dermal, Inhalation |
1, 2, 3 |
|
Exclamation Mark – Harmful
Used for hazards of lower grade severity in which the adverse effects are not as consequential |
Acute Toxicity – Oral, Dermal, Inhalation | 4 |
| Skin Irritation | 2, 3 | |
| Eye Irritation | 2A | |
| Skin Sensitization | 1 | |
Specific target organ toxicity following single exposure for
|
3 | |
|
Physical Hazards |
Explosives | Divisions 1.5, 1.6 |
|
Flammable Gases |
2 |
|
|
Self-reactive substances |
G |
|
|
Organic Peroxides |
G |
|
|
Health Hazards |
Acute Toxicity – oral, dermal, inhalation | 5 |
| Eye irritation |
2B |
|
|
Reproductive Toxicity
|
||
|
Environmental Hazards
|
Acute hazards to aquatic environment |
3, 4 |
| Chronic hazards to aquatic environment |
3, 4 |